

In this tutorial, we will learn how to validate Spring boot REST API requests using Hibernate validator.
In Java, the Java Bean Validation framework has become the de-facto standard for handling validations in
Java projects.
JSR 380 is a specification of the Java API for bean validation and this ensures that the properties of a
bean meet specific criteria, using annotations such as @NotNull, @Min, and @Max.
Hibernate Validator is the reference implementation of the validation API.
Check out the complete list here athttps://www.sourcecodeexamples.net/2021/03/java-bean-validation-annotation-list.html
Spring boot provides good integration support with Hibernate validator.
We will use Hibernate Validator, which is one of the reference implementations of the bean validation
API.
Starting with Boot 2.3, we need to explicitly add the spring-boot-starter-validation dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>Let's create a step-by-step example to demonstrate how to validate the Spring boot REST API request using Hibernate validator.
Use the below guide to create a Spring boot project in Eclipse STS IDE:
=> Create Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite [STS]
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Let's create a User class and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Table(name = "users")
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "name", nullable = false)
// user name should not be null or empty
// user name should have at least 2 characters
@NotEmpty
@Size(min = 2, message = "user name should have at least 2 characters")
private String name;
// email should be a valid email format
// email should not be null or empty
@NotEmpty
@Email
private String email;
// password should not be null or empty
// password should have at least 8 characters
@NotEmpty
@Size(min = 8, message = "password should have at least 8 characters")
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, String email, String password) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.password = password;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}Note that we have added Java bean annotations to the User domain entity:
Spring boot automatically configure database details for H2 in-memory database so we no need to explicitly add the database configuration in the application.properties file.
Let's create a UserRepository class which talk with database. Add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository< User, Long>{
Let's create UserService and add the following code to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public User createUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}Let's create a UserController class and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.UserService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping("users")
public ResponseEntity createUser(@Valid @RequestBody User user){
User savedUser = userService.createUser(user);
return new ResponseEntity(savedUser, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
} Note that we enable validation on Spring Rest Controller by adding @Valid annotation in addition to @RequestBody.
Let's create a ValidationHandler to customize the validation response.
To customize response validation, we need to extend ResponseEntityExceptionHandler class and override
handleMethodArgumentNotValid(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) method.
Let's create ValidationHandler class and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ValidationHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler{
@Override
protected ResponseEntity< Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex,
HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
Map< String, String> errors = new HashMap< >();
ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().forEach((error) ->{
String fieldName = ((FieldError) error).getField();
String message = error.getDefaultMessage();
errors.put(fieldName, message);
});
return new ResponseEntity< Object>(errors, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}Run the Spring boot application with the main class:
package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootValidationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootValidationApplication.class, args);
}
}The below screenshot shows the validation of Spring boot REST API using Hibernate validator:
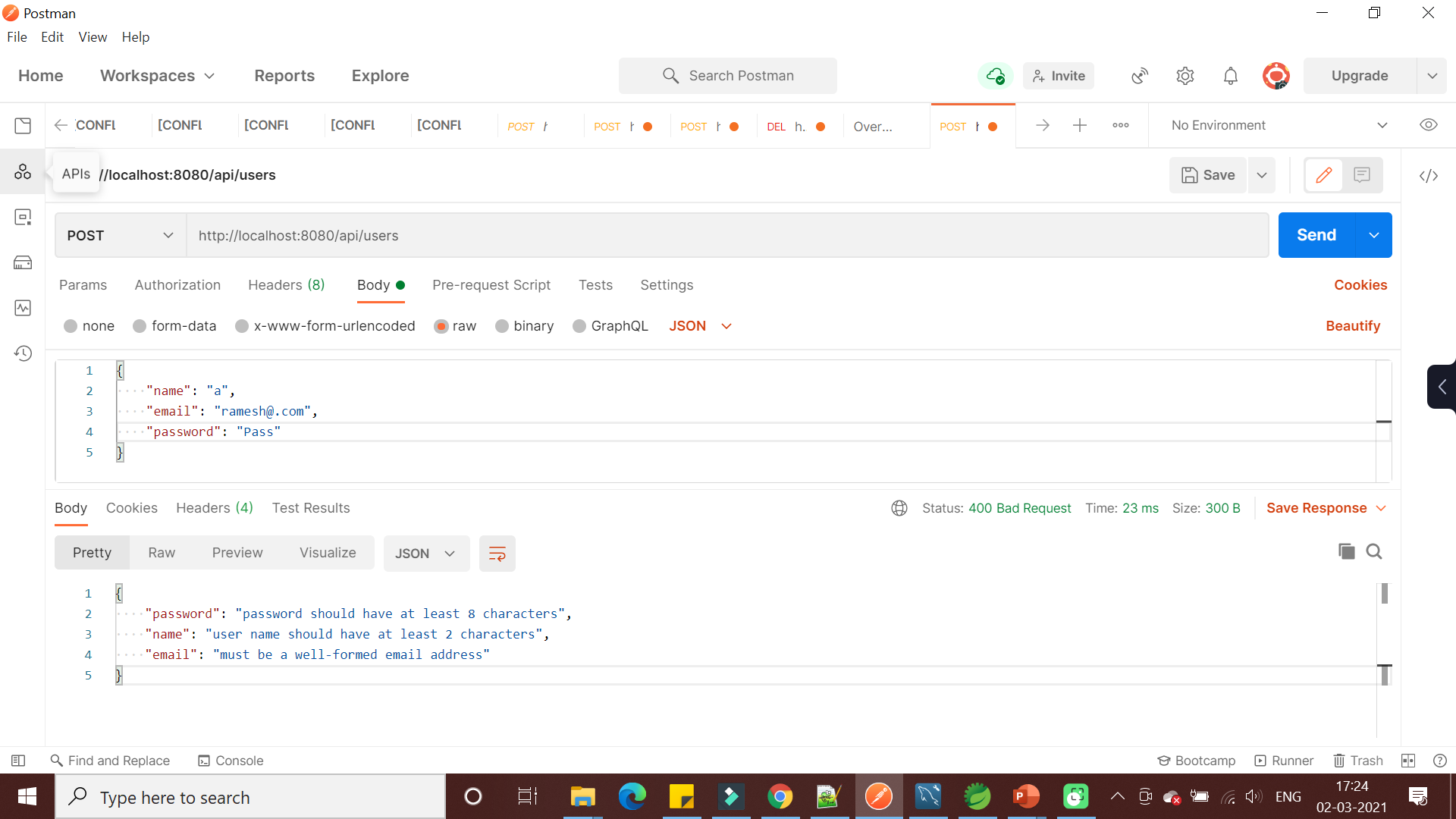
In this tutorial, we learned how to validate Spring boot REST API requests using Hibernate validator.
The source code of this tutorial available on my GitHub repositoryhttps://github.com/Sai/springboot-validation
Starting with Boot 2.3, we need to explicitly add the spring-boot-starter-validation dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>